Introduction
In this post, we’ll cover how to start using Large Language Models (LLMs) for free, locally on your computer.
LLMs are essentially predictive text programs, where general usage involves providing a starting point (prompt), and then predicts how the body of text may continue.
Due to how LLMs are trained, they need tons of data to create machine learning models that can predict these words. As such, using platforms like OpenAI’s ChatGPT means that all of the information included in your chats is likely to be used to train how an LLM should respond to prompts. If you’re not a fan of this, and/or want to run models that don’t cost an arm and a leg, this might be a good starting point.
Install Ollama
Installation instructions should be available at https://ollama.com/download, where you can download an installer for Windows and MacOS. Linux can be done simply via the command line.
Linux
|
|
If you have an NVIDIA graphics card, I recommend you install NVIDIA CUDA toolkit, to take advantage of additional performance. This is optional.
You may need to start Ollama with ollama serve after installing.
Downloading a Model
Now that we have Ollama installed, we must download a compatible model from https://ollama.com/search.
Models are essentially the raw weights used in the neural network that tweak the output for each individual neuron in the neural network. Think of them like brains, where they are generally better, the more data the model was trained on.
LLMs’ response quality is mainly based on the information the model was trained on. For example, the qwen series of models are trained on code accessible by the internet. As a result, it’s tuned to be able to produce code. Most models, are trained on generic text on the internet and will have very limited ability to produce code. One of the generic ones I like is llama3.2. If you’re running this model on a low-resource machine, phi might be a good option. That said, the smaller versions of llama3.2 should still run, so long as you have memory, albeit slowly.
Once you’ve picked a model, you can download it using the model’s ID:
|
|

You can check the license on the model page, to ensure you are allowed to use it for your intended purposes.
Invoking a Model
In this section, provide instructions for how to invoke a model using OLLAMa. This could include information on how to input text or data into the model and what kind of output can be expected.
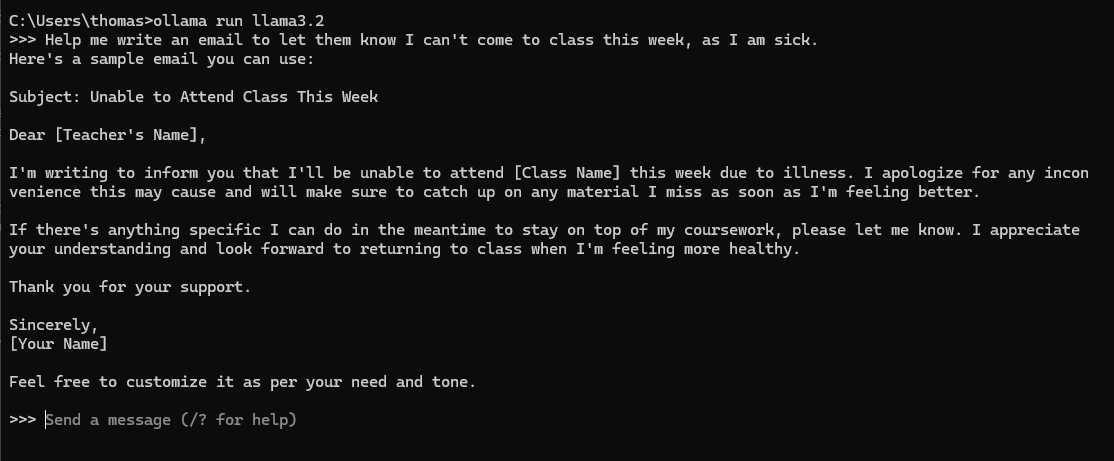
Now, to run the model you just downloaded, run the following.
|
|
Then you can enter a prompt, and get a response.
Installing OpenWebUI
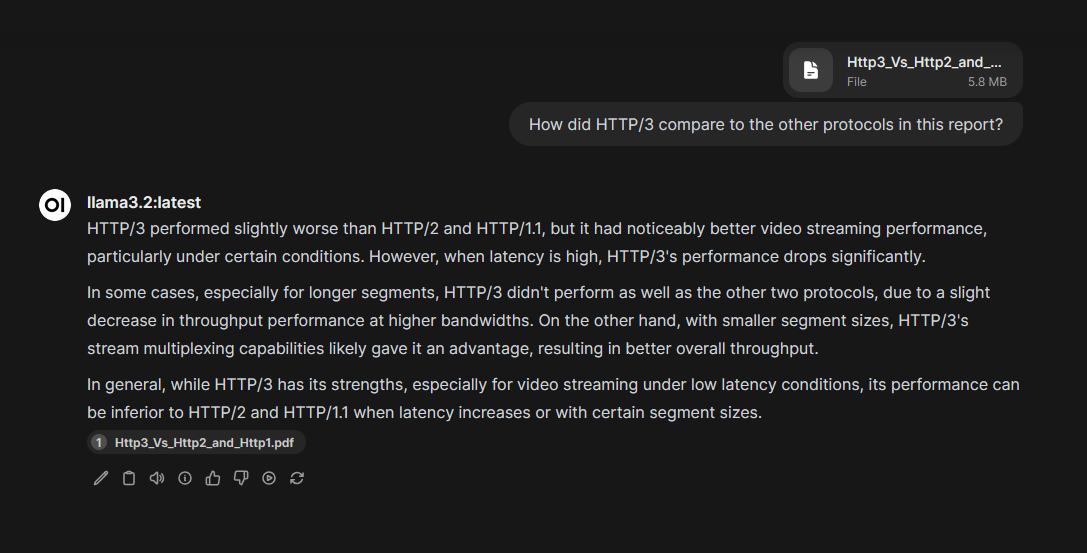
Open WebUI is a powerful web interface that can communicate with Ollama’s API to use it as a host to run LLMs on. Open WebUI contains a database of previous chats, and supports adding documents to a chat, allowing you to ask the LLM questions about the contents of the document.
You can find the installation instructions here, I recommend using either Docker or Python using venv to manage the dependencies.